Low-coding as the source of endless possibilities
Low-code platforms can help development teams work faster, more efficiently, and increase enterprise-class software production by providing opportunities for non-professional developers as well.
- The research firm Gartner predicts that by 2024, 80% of technical products and services will be developed by people who are not tech professionals. According to them by 2025, low-code application platforms are expected to remain the largest component of the low-code development technology family of products.
How low-coding has become a revolutionary phenomenon in software development?
The history of software development is the story of making technology more accessible and easier to use. The term “low-code development” was introduced in 2014 by a market research institute (Forrester Group) as a generic term for several providers. Forrester characterizes low-code platforms as those “products and/or cloud services for application development that employ visual, declarative techniques instead of programming". When using low-code software one doesn't have to tell what to do in a programming language. Naturally, if the software requires less programming to make, it also takes less money and time. Moreover, it enables millions of people worldwide to “write” software, but at least to transform an existing one.
 Technology is the foundation of every modern business, thus everyone is aware of its importance. Even though many people care about technology, they don’t necessarily understand its depths. The greater the access to technology, the more developers are considered experts. The low-code boom offers people powerful tools that reinforce the need for developers to manage, integrate, extend, and further develop these tools. So, the whole process is faster and cheaper. It’s as if the number of software developers was suddenly multiplying. Low-coding could even reduce the global IT gap. The more people have access to these tools and will be able to use them, the faster the innovation will be. Accelerating digital transformation and better responsiveness to business change are the primary drivers of low-code and platform take-up. In addition, reducing its reliance on hard-to-reach developer competencies and avoiding the constraints associated with legacy systems have played a role in its popularity.
Technology is the foundation of every modern business, thus everyone is aware of its importance. Even though many people care about technology, they don’t necessarily understand its depths. The greater the access to technology, the more developers are considered experts. The low-code boom offers people powerful tools that reinforce the need for developers to manage, integrate, extend, and further develop these tools. So, the whole process is faster and cheaper. It’s as if the number of software developers was suddenly multiplying. Low-coding could even reduce the global IT gap. The more people have access to these tools and will be able to use them, the faster the innovation will be. Accelerating digital transformation and better responsiveness to business change are the primary drivers of low-code and platform take-up. In addition, reducing its reliance on hard-to-reach developer competencies and avoiding the constraints associated with legacy systems have played a role in its popularity.
Low-code vs. No-code: what are the differences?
We all have heard of the hype surrounding low-code and no-code platforms lately. No-code platforms promise the user that they make software development as easy as using Word or PowerPoint, so the average business user can move projects forward without the added cost (in money and time) of an engineering team. But this kind of functionality has heavy limitations. As no two no-code platforms are alike they need very clear requirements. Stiff templates also limit the possibilities with no real customization.
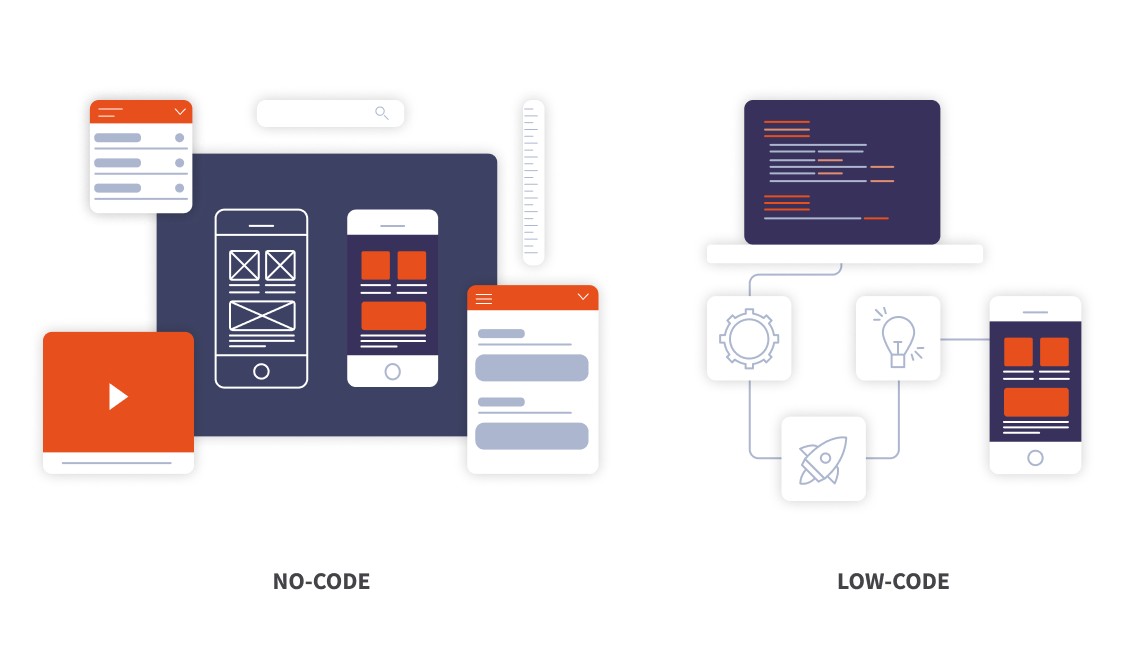 Unlike no-code platforms, low-code platforms still require some programming skills, but promise to accelerate software development by allowing developers to work with pre-written code components. A feature of low-coding is that the building of any business project becomes much faster than in a traditional, custom software development method. The exact competencies that are needed to develop low-code applications is platform-dependent.
Unlike no-code platforms, low-code platforms still require some programming skills, but promise to accelerate software development by allowing developers to work with pre-written code components. A feature of low-coding is that the building of any business project becomes much faster than in a traditional, custom software development method. The exact competencies that are needed to develop low-code applications is platform-dependent.
Some tools act as a kind of development framework, so their goal is not to replace programmers, just to make their work easier. And some platforms require only minimal programming knowledge; in addition, we may come across ones that require almost no programming competence at all (the latter is increasingly referred to as no-coding as seen above).
Low-code “drag and drop” platforms from a practical approach – what are the real benefits?
The demand for rapid and agile application development has always been high as companies rely on their IT organizations to develop and deliver ready-to-manufacture solutions.
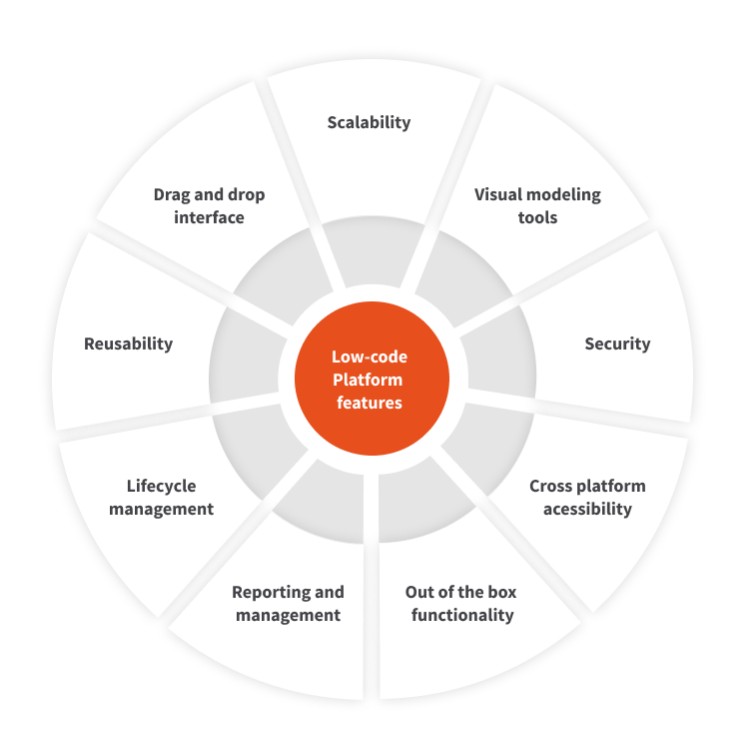 The low-code development platform is an application that provides a graphical user interface for programming, thereby accelerating the production of a code with reduced classical programming efforts. These tools help one to develop code quickly, while minimizing manual coding effort. It is easy to understand why it is inevitable for a business: these platforms not only help with coding, but also with quick setup and installation.
The low-code development platform is an application that provides a graphical user interface for programming, thereby accelerating the production of a code with reduced classical programming efforts. These tools help one to develop code quickly, while minimizing manual coding effort. It is easy to understand why it is inevitable for a business: these platforms not only help with coding, but also with quick setup and installation.
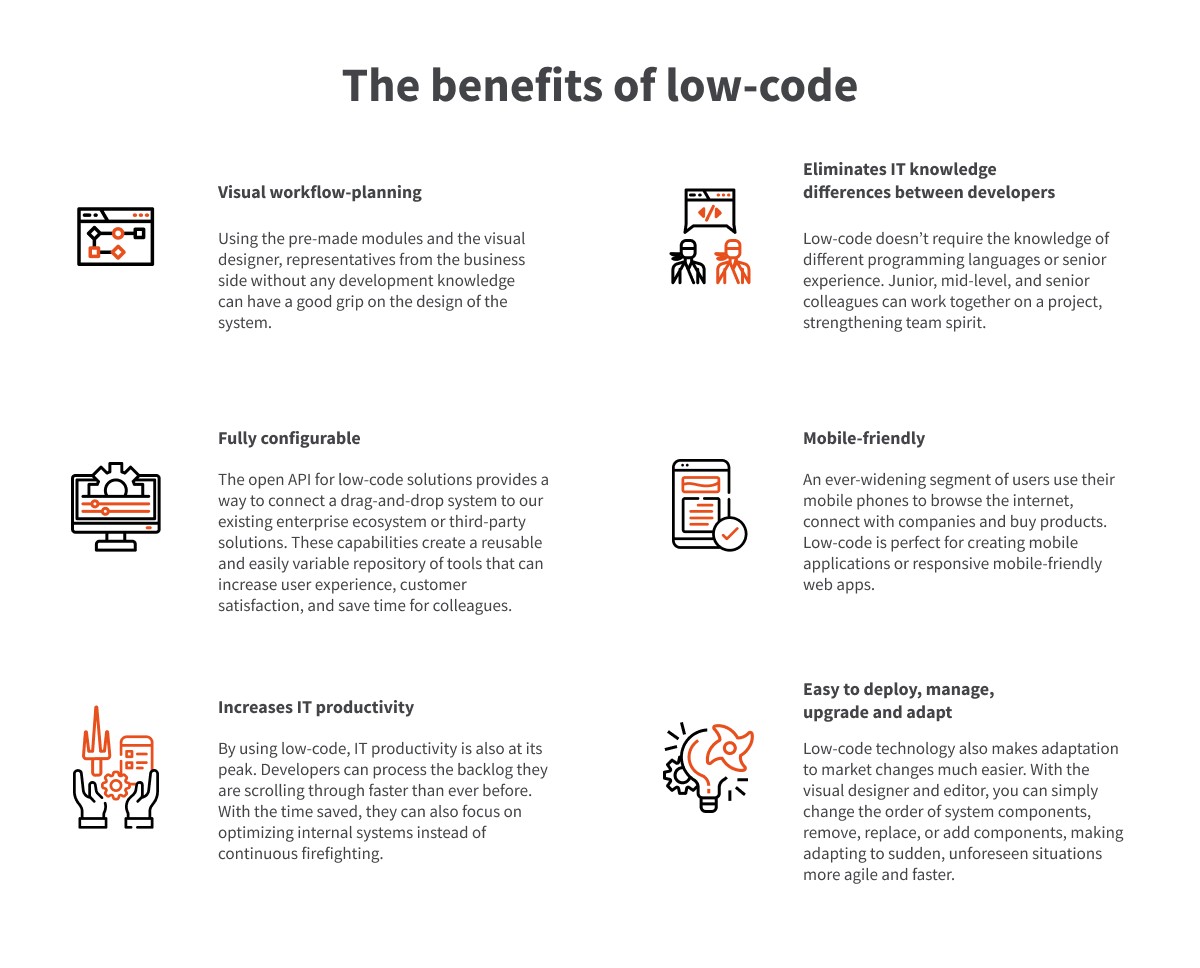 At one end of the scale are visual tools, including no-code solutions, that allow one to create business applications without more serious programming knowledge. These might be ERP solutions which can be customized with great freedom. At the other end of the low-code scale are the professional development platforms which support the work of an agile team effectively; largely freeing them from tedious and monotonous tasks.
At one end of the scale are visual tools, including no-code solutions, that allow one to create business applications without more serious programming knowledge. These might be ERP solutions which can be customized with great freedom. At the other end of the low-code scale are the professional development platforms which support the work of an agile team effectively; largely freeing them from tedious and monotonous tasks.
According to Forrester Wave’s 2021 Q2 report the 3 most important factors in considering low-coding are:
- ● Both data-centric and process-centric development patterns matter the same level so with the right partner simple projects should be painless, complex projects well planned and efficient as a result.
- ● Developers should provide tools suitable on a larger spectrum.
- ● Platforms and providers have to be able to meet specific infrastructure and requirements of the process.
We would like to help you choose from all the providers. Based on Forrester’s recent research the best usable platforms are given by: Mendix, OutSystems, Microsoft and ServiceNow. Also really strong performers on the market: Salesforce, Pegasystems, Appian, HCL Software, AgilePoint, Unqork, Oracle and Thinkwise.
From the aspect of security
Low-code platforms accelerate the delivery of applications, but are they secure? The answer is a bit more complicated than expected.
 One of the biggest barriers of the development of enterprise software has always been that business users do not have a clear understanding of programming, and developers do not understand the processes of the business industry. The low-code platform is part of the IT infrastructure, subject to security, integration, and deployment rules – if the user creates something in it, it cannot harm enterprise systems. So, one doesn't have to pay the smoothness or security of operations for the speed of development.
One of the biggest barriers of the development of enterprise software has always been that business users do not have a clear understanding of programming, and developers do not understand the processes of the business industry. The low-code platform is part of the IT infrastructure, subject to security, integration, and deployment rules – if the user creates something in it, it cannot harm enterprise systems. So, one doesn't have to pay the smoothness or security of operations for the speed of development.
What can this low-code boost possibly mean for security teams? According to experts there are three key points companies have to consider:
1. If application developers are suddenly not part of the development team, it takes time for a company to understand the organization’s low-code strategy, such as who is developing which types of applications, and where they are in the team.
- 2. It may be time to expand the network again – get to know the organization’s developers accurately and start building the credibility of the security team with new stakeholders.
- 3. Security training is evolving in case of low-code development: citizen developers are less likely to introduce an SQL injection than poorly configuring permissions or leaking data. It is necessary to pay attention to the security principles that best suit the application structure of low-code developers.
Predictions
The essence and main effect of the low-code method are to accelerate development by essentially recycling the experience already accumulated in the form of modules. Experts say this is more of a help to an already burdened IT team than a threat. The representatives of the business side, who formulate the needs, put it together from existing modules according to the developed business logic – they are called citizen developers officially. This, of course, requires special competencies, but most people working on the business side already own them.
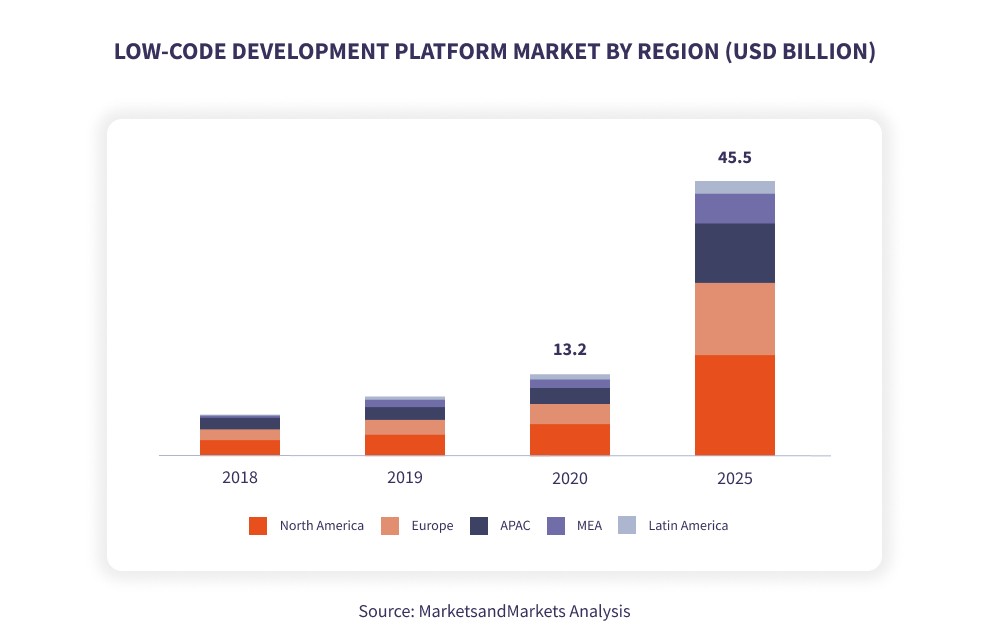
According to Forrester, the global market for low-coding platforms is growing rapidly, averaging 40 percent annually, and will exceed $21 billion by 2022. Low-code that democratizes development and spurs transportation will become widespread if LCAP (Low-Code Application Platforms) suppliers also provide companies with sufficiently effective tools to manage usage.
 Some questions are arising with this boom of low-coding. Can the rise of the "citizen developer" and AI lead to the end of the professional developer role? Low-code development has been a success in the industry, but this is not the first time in the developer world that disruptions like this are experienced. The ability to adapt to the constant development of technology means that truly good professionals are more valuable than ever.
Some questions are arising with this boom of low-coding. Can the rise of the "citizen developer" and AI lead to the end of the professional developer role? Low-code development has been a success in the industry, but this is not the first time in the developer world that disruptions like this are experienced. The ability to adapt to the constant development of technology means that truly good professionals are more valuable than ever.
2021-08-10
Low-coding as the source of endless possibilities
7 min
Services and products we used
Share

